Get 100% Passing Success With True Professional-Data-Engineer Exam! [Jun-2021]
Google Professional-Data-Engineer PDF Questions - Exceptional Practice To Google Certified Professional Data Engineer Exam
NEW QUESTION 95
Which of these is not a supported method of putting data into a partitioned table?
- A. If you have existing data in a separate file for each day, then create a partitioned table and upload each file into the appropriate partition.
- B. Create a partitioned table and stream new records to it every day.
- C. Use ORDER BY to put a table's rows into chronological order and then change the table's type to "Partitioned".
- D. Run a query to get the records for a specific day from an existing table and for the destination table, specify a partitioned table ending with the day in the format "$YYYYMMDD".
Answer: C
Explanation:
You cannot change an existing table into a partitioned table. You must create a partitioned table from scratch. Then you can either stream data into it every day and the data will automatically be put in the right partition, or you can load data into a specific partition by using "$YYYYMMDD" at the end of the table name.
Reference: https://cloud.google.com/bigquery/docs/partitioned-tables
NEW QUESTION 96
What is the recommended action to do in order to switch between SSD and HDD storage for your Google Cloud Bigtable instance?
- A. the selection is final and you must resume using the same storage type
- B. create a third instance and sync the data from the two storage types via batch jobs
- C. export the data from the existing instance and import the data into a new instance
- D. run parallel instances where one is HDD and the other is SDD
Answer: C
Explanation:
When you create a Cloud Bigtable instance and cluster, your choice of SSD or HDD storage for the cluster is permanent. You cannot use the Google Cloud Platform Console to change the type of storage that is used for the cluster.
If you need to convert an existing HDD cluster to SSD, or vice-versa, you can export the data from the existing instance and import the data into a new instance. Alternatively, you can write a Cloud Dataflow or Hadoop MapReduce job that copies the data from one instance to another.
Reference: https://cloud.google.com/bigtable/docs/choosing-ssd-hdd-
NEW QUESTION 97
You work for a shipping company that has distribution centers where packages move on delivery lines to route them properly. The company wants to add cameras to the delivery lines to detect and track any visual damage to the packages in transit. You need to create a way to automate the detection of damaged packages and flag them for human review in real time while the packages are in transit. Which solution should you choose?
- A. Train an AutoML model on your corpus of images, and build an API around that model to integrate with the package tracking applications.
- B. Use the Cloud Vision API to detect for damage, and raise an alert through Cloud Functions. Integrate the package tracking applications with this function.
- C. Use TensorFlow to create a model that is trained on your corpus of images. Create a Python notebook in Cloud Datalab that uses this model so you can analyze for damaged packages.
- D. Use BigQuery machine learning to be able to train the model at scale, so you can analyze the packages in batches.
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 98
Suppose you have a table that includes a nested column called "city" inside a column called "person", but when you try to submit the following query in BigQuery, it gives you an error. SELECT person FROM
`project1.example.table1` WHERE city = "London" How would you correct the error?
- A. Add ", UNNEST(city)" before the WHERE clause.
- B. Change "person" to "person.city".
- C. Change "person" to "city.person".
- D. Add ", UNNEST(person)" before the WHERE clause.
Answer: D
Explanation:
To access the person.city column, you need to "UNNEST(person)" and JOIN it to table1 using a comma.
Reference:
https://cloud.google.com/bigquery/docs/reference/standard-sql/migrating-from-legacy- sql#nested_repeated_results
NEW QUESTION 99
Your company is loading comma-separated values (CSV) files into Google BigQuery. The data is fully
imported successfully; however, the imported data is not matching byte-to-byte to the source file. What is
the most likely cause of this problem?
- A. The CSV data has not gone through an ETL phase before loading into BigQuery.
- B. The CSV data loaded in BigQuery is not flagged as CSV.
- C. The CSV data loaded in BigQuery is not using BigQuery's default encoding.
- D. The CSV data has invalid rows that were skipped on import.
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 100
An organization maintains a Google BigQuery dataset that contains tables with user-level data. They want
to expose aggregates of this data to other Google Cloud projects, while still controlling access to the user-
level data. Additionally, they need to minimize their overall storage cost and ensure the analysis cost for
other projects is assigned to those projects. What should they do?
- A. Create and share a new dataset and table that contains the aggregate results.
- B. Create and share an authorized view that provides the aggregate results.
- C. Create dataViewer Identity and Access Management (IAM) roles on the dataset to enable sharing.
- D. Create and share a new dataset and view that provides the aggregate results.
Answer: C
Explanation:
Explanation/Reference:
Reference: https://cloud.google.com/bigquery/docs/access-control
NEW QUESTION 101
You are a head of BI at a large enterprise company with multiple business units that each have different priorities and budgets. You use on-demand pricing for BigQuery with a quota of 2K concurrent on-demand slots per project. Users at your organization sometimes don't get slots to execute their query and you need to correct this. You'd like to avoid introducing new projects to your account.
What should you do?
- A. Switch to flat-rate pricing and establish a hierarchical priority model for your projects.
- B. Increase the amount of concurrent slots per project at the Quotas page at the Cloud Console.
- C. Convert your batch BQ queries into interactive BQ queries.
- D. Create an additional project to overcome the 2K on-demand per-project quota.
Answer: A
Explanation:
Explanation/Reference:
Reference https://cloud.google.com/blog/products/gcp/busting-12-myths-about-bigquery
NEW QUESTION 102
Case Study: 1 - Flowlogistic
Company Overview
Flowlogistic is a leading logistics and supply chain provider. They help businesses throughout the world manage their resources and transport them to their final destination. The company has grown rapidly, expanding their offerings to include rail, truck, aircraft, and oceanic shipping.
Company Background
The company started as a regional trucking company, and then expanded into other logistics market.
Because they have not updated their infrastructure, managing and tracking orders and shipments has become a bottleneck. To improve operations, Flowlogistic developed proprietary technology for tracking shipments in real time at the parcel level. However, they are unable to deploy it because their technology stack, based on Apache Kafka, cannot support the processing volume. In addition, Flowlogistic wants to further analyze their orders and shipments to determine how best to deploy their resources.
Solution Concept
Flowlogistic wants to implement two concepts using the cloud:
Use their proprietary technology in a real-time inventory-tracking system that indicates the location of their loads Perform analytics on all their orders and shipment logs, which contain both structured and unstructured data, to determine how best to deploy resources, which markets to expand info. They also want to use predictive analytics to learn earlier when a shipment will be delayed.
Existing Technical Environment
Flowlogistic architecture resides in a single data center:
Databases
8 physical servers in 2 clusters
SQL Server - user data, inventory, static data
3 physical servers
Cassandra - metadata, tracking messages
10 Kafka servers - tracking message aggregation and batch insert
Application servers - customer front end, middleware for order/customs 60 virtual machines across 20 physical servers Tomcat - Java services Nginx - static content Batch servers Storage appliances iSCSI for virtual machine (VM) hosts Fibre Channel storage area network (FC SAN) ?SQL server storage Network-attached storage (NAS) image storage, logs, backups Apache Hadoop /Spark servers Core Data Lake Data analysis workloads
20 miscellaneous servers
Jenkins, monitoring, bastion hosts,
Business Requirements
Build a reliable and reproducible environment with scaled panty of production. Aggregate data in a centralized Data Lake for analysis Use historical data to perform predictive analytics on future shipments Accurately track every shipment worldwide using proprietary technology Improve business agility and speed of innovation through rapid provisioning of new resources Analyze and optimize architecture for performance in the cloud Migrate fully to the cloud if all other requirements are met Technical Requirements Handle both streaming and batch data Migrate existing Hadoop workloads Ensure architecture is scalable and elastic to meet the changing demands of the company.
Use managed services whenever possible
Encrypt data flight and at rest
Connect a VPN between the production data center and cloud environment SEO Statement We have grown so quickly that our inability to upgrade our infrastructure is really hampering further growth and efficiency. We are efficient at moving shipments around the world, but we are inefficient at moving data around.
We need to organize our information so we can more easily understand where our customers are and what they are shipping.
CTO Statement
IT has never been a priority for us, so as our data has grown, we have not invested enough in our technology. I have a good staff to manage IT, but they are so busy managing our infrastructure that I cannot get them to do the things that really matter, such as organizing our data, building the analytics, and figuring out how to implement the CFO' s tracking technology.
CFO Statement
Part of our competitive advantage is that we penalize ourselves for late shipments and deliveries. Knowing where out shipments are at all times has a direct correlation to our bottom line and profitability.
Additionally, I don't want to commit capital to building out a server environment.
Flowlogistic's management has determined that the current Apache Kafka servers cannot handle the data volume for their real-time inventory tracking system. You need to build a new system on Google Cloud Platform (GCP) that will feed the proprietary tracking software. The system must be able to ingest data from a variety of global sources, process and query in real-time, and store the data reliably. Which combination of GCP products should you choose?
- A. Cloud Pub/Sub, Cloud Dataflow, and Local SSD
- B. Cloud Load Balancing, Cloud Dataflow, and Cloud Storage
- C. Cloud Pub/Sub, Cloud Dataflow, and Cloud Storage
- D. Cloud Pub/Sub, Cloud SQL, and Cloud Storage
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 103
Which of the following IAM roles does your Compute Engine account require to be able to run pipeline jobs?
- A. dataflow.viewer
- B. dataflow.compute
- C. dataflow.developer
- D. dataflow.worker
Answer: D
Explanation:
Explanation
The dataflow.worker role provides the permissions necessary for a Compute Engine service account to execute work units for a Dataflow pipeline Reference: https://cloud.google.com/dataflow/access-control
NEW QUESTION 104
You have some data, which is shown in the graphic below. The two dimensions are X and Y, and the
shade of each dot represents what class it is. You want to classify this data accurately using a linear
algorithm. To do this you need to add a synthetic feature. What should the value of that feature be?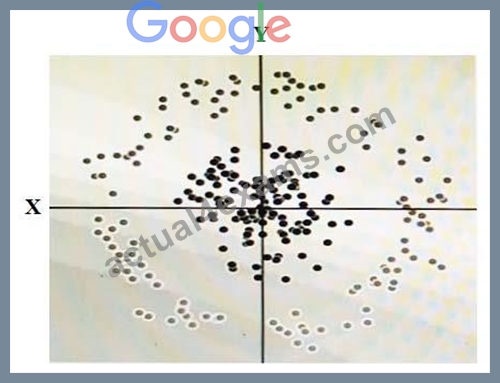
- A. Y^2
- B. X^2
- C. cos(X)
- D. X^2+Y^2
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 105
Your company is migrating their 30-node Apache Hadoop cluster to the cloud. They want to re-use
Hadoop jobs they have already created and minimize the management of the cluster as much as possible.
They also want to be able to persist data beyond the life of the cluster. What should you do?
- A. Create a Cloud Dataproc cluster that uses the Google Cloud Storage connector.
- B. Create a Hadoop cluster on Google Compute Engine that uses persistent disks.
- C. Create a Google Cloud Dataflow job to process the data.
- D. Create a Hadoop cluster on Google Compute Engine that uses Local SSD disks.
- E. Create a Google Cloud Dataproc cluster that uses persistent disks for HDFS.
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 106
You need to deploy additional dependencies to all of a Cloud Dataproc cluster at startup using an existing initialization action. Company security policies require that Cloud Dataproc nodes do not have access to the Internet so public initialization actions cannot fetch resources. What should you do?
- A. Use an SSH tunnel to give the Cloud Dataproc cluster access to the Internet
- B. Deploy the Cloud SQL Proxy on the Cloud Dataproc master
- C. Use Resource Manager to add the service account used by the Cloud Dataproc cluster to the Network User role
- D. Copy all dependencies to a Cloud Storage bucket within your VPC security perimeter
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 107
You have enabled the free integration between Firebase Analytics and Google BigQuery. Firebase now automatically creates a new table daily in BigQuery in the format app_events_YYYYMMDD.You want to query all of the tables for the past 30 days in legacy SQL. What should you do?
- A. Use the TABLE_DATE_RANGEfunction
- B. Use the WHERE_PARTITIONTIMEpseudo column
- C. Use WHEREdate BETWEEN YYYY-MM-DD AND YYYY-MM-DD
- D. Use SELECT IF.(date >= YYYY-MM-DD AND date <= YYYY-MM-DD
Answer: A
Explanation:
Explanation/Reference: https://cloud.google.com/blog/products/gcp/using-bigquery-and-firebase-analytics-to-understand- your-mobile-app?hl=am
NEW QUESTION 108
You are designing a data processing pipeline. The pipeline must be able to scale automatically as load increases. Messages must be processed at least once and must be ordered within windows of 1 hour.
How should you design the solution?
- A. Use Cloud Pub/Sub for message ingestion and Cloud Dataflow for streaming analysis.
- B. Use Cloud Pub/Sub for message ingestion and Cloud Dataproc for streaming analysis.
- C. Use Apache Kafka for message ingestion and use Cloud Dataproc for streaming analysis.
- D. Use Apache Kafka for message ingestion and use Cloud Dataflow for streaming analysis.
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 109
You designed a database for patient records as a pilot project to cover a few hundred patients in three clinics.
Your design used a single database table to represent all patients and their visits, and you used self-joins to generate reports. The server resource utilization was at 50%. Since then, the scope of the project has expanded.
The database must now store 100 times more patient records. You can no longer run the reports, because they either take too long or they encounter errors with insufficient compute resources. How should you adjust the database design?
- A. Add capacity (memory and disk space) to the database server by the order of 200.
- B. Normalize the master patient-record table into the patient table and the visits table, and create other necessary tables to avoid self-join.
- C. Partition the table into smaller tables, with one for each clinic. Run queries against the smaller table pairs, and use unions for consolidated reports.
- D. Shard the tables into smaller ones based on date ranges, and only generate reports with prespecified date ranges.
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 110
You decided to use Cloud Datastore to ingest vehicle telemetry data in real time. You want to build a storage system that will account for the long-term data growth, while keeping the costs low. You also want to create snapshots of the data periodically, so that you can make a point-in-time (PIT) recovery, or clone a copy of the data for Cloud Datastore in a different environment. You want to archive these snapshots for a long time.
Which two methods can accomplish this? (Choose two.)
- A. Write an application that uses Cloud Datastore client libraries to read all the entities. Format the exported data into a JSON file. Apply compression before storing the data in Cloud Source Repositories.
- B. Use managed export, and then import to Cloud Datastore in a separate project under a unique namespace reserved for that export.
- C. Use managed export, and then import the data into a BigQuery table created just for that export, and delete temporary export files.
- D. Write an application that uses Cloud Datastore client libraries to read all the entities. Treat each entity as a BigQuery table row via BigQuery streaming insert. Assign an export timestamp for each export, and attach it as an extra column for each row. Make sure that the BigQuery table is partitioned using the export timestamp column.
- E. Use managed export, and store the data in a Cloud Storage bucket using Nearline or Coldline class.
Answer: A,C
NEW QUESTION 111
What are two methods that can be used to denormalize tables in BigQuery?
- A. 1) Join tables into one table; 2) Use nested repeated fields
- B. 1) Use nested repeated fields; 2) Use a partitioned table
- C. 1) Split table into multiple tables; 2) Use a partitioned table
- D. 1) Use a partitioned table; 2) Join tables into one table
Answer: A
Explanation:
Explanation
The conventional method of denormalizing data involves simply writing a fact, along with all its dimensions, into a flat table structure. For example, if you are dealing with sales transactions, you would write each individual fact to a record, along with the accompanying dimensions such as order and customer information.
The other method for denormalizing data takes advantage of BigQuery's native support for nested and repeated structures in JSON or Avro input data. Expressing records using nested and repeated structures can provide a more natural representation of the underlying data. In the case of the sales order, the outer part of a JSON structure would contain the order and customer information, and the inner part of the structure would contain the individual line items of the order, which would be represented as nested, repeated elements.
Reference: https://cloud.google.com/solutions/bigquery-data-warehouse#denormalizing_data
NEW QUESTION 112
Your company is using WHILECARD tables to query data across multiple tables with similar names. The SQL statement is currently failing with the following error:
# Syntax error : Expected end of statement but got "-" at [4:11] SELECT age FROM bigquery-public-data.noaa_gsod.gsod WHERE age != 99 AND_TABLE_SUFFIX = `1929' ORDER BY age DESC Which table name will make the SQL statement work correctly?
- A. `bigquery-public-data.noaa_gsod.gsod'*
- B. bigquery-public-data.noaa_gsod.gsod*
- C. `bigquery-public-data.noaa_gsod.gsod*`
- D. `bigquery-public-data.noaa_gsod.gsod`
Answer: C
Explanation:
It follows the correct wildcard syntax of enclosing the table name in backticks and including the * wildcard character.
NEW QUESTION 113
You have some data, which is shown in the graphic below. The two dimensions are X and Y, and the shade of each dot represents what class it is. You want to classify this data accurately using a linear algorithm. To do this you need to add a synthetic feature. What should the value of that feature be?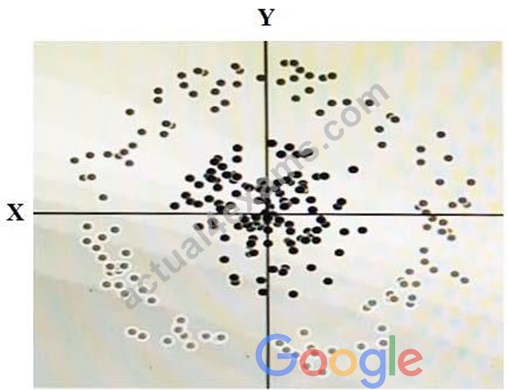
- A. Y^2
- B. X^2
- C. cos(X)
- D. X^2+Y^2
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 114
......
Professional-Data-Engineer dumps - Actual4Exams - 100% Passing Guarantee: https://www.actual4exams.com/Professional-Data-Engineer-valid-dump.html
Fast, Hands-On Professional-Data-Engineer exam: https://drive.google.com/open?id=1jzCnkLVfBAzo54WOvf5UBQjlJQHy55_t

